When digitising, you might have come across strange rainbow patterns. These patterns are known as moiré (from French moiré [mwaˈʀe], “moiré, marbled”) and can cause many headaches. In this article, we will look at what moiré is and what causes it.
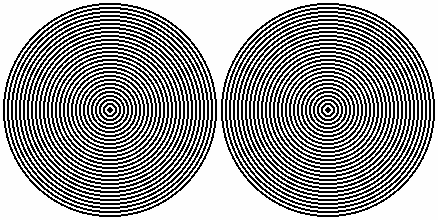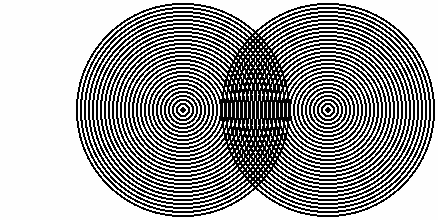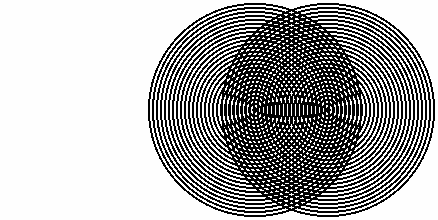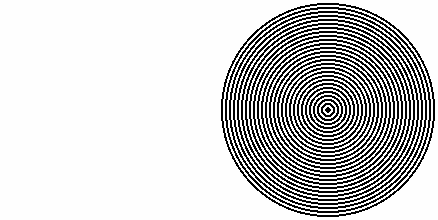
The moiré effect occurs when the item being captured contains a detailed pattern that does not play along with the pattern of the imaging sensor. With two separate patterns overlaid on top of each other, a third, false pattern emerges in the form of ‘moiré pattern’.
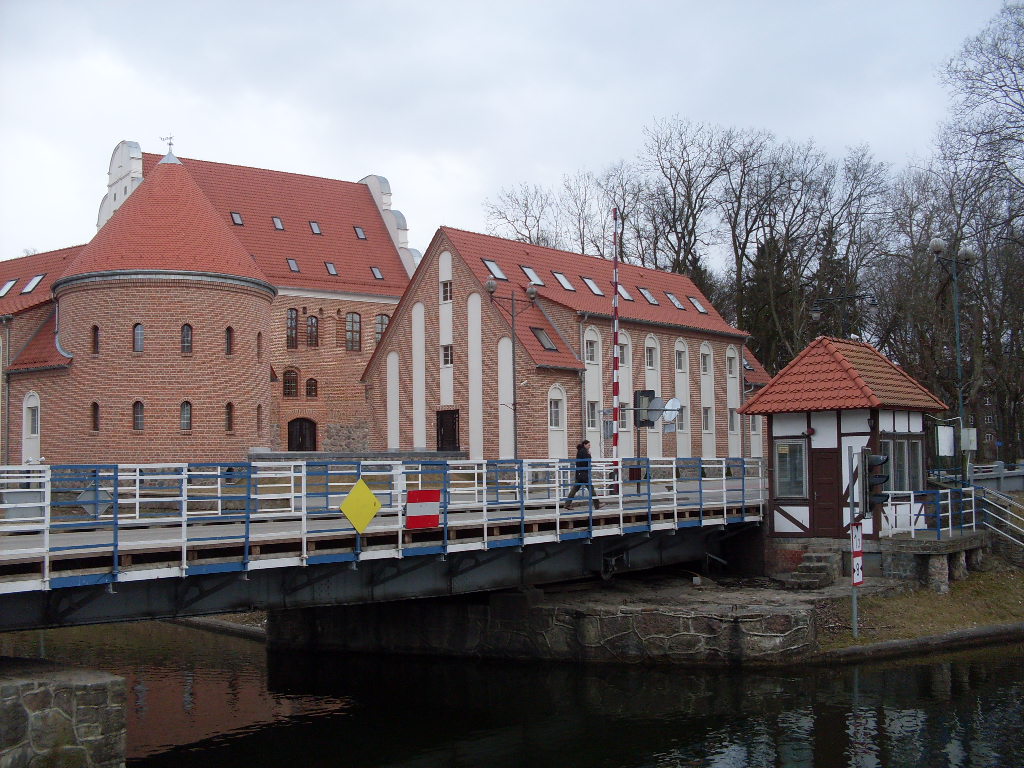
The moiré effect can be clearly seen in the image below: The periodic structures of the sensor are superimposed on those of the brick pattern on the building, forming a peculiar striped pattern.
Source: Wikimedia Commons (unchanged) Schloß Lötzen mit Drehbrücke im April 2012 Copyright: Colin Pelka Public Domain
The moiré effect also often is a challenge when digitising newspapers since in newspaper production halftone used for photos to be printed, especially on more absorbent papers like newsprint. Since ink on newsprint dries by absorption, photos are made of varying size dots in a coarse pattern. When you made an image of the halftone image, the conflicting dot patterns resulted in a moiré pattern.
How to avoid the moiré effect:
Sometimes it is already sufficient to slightly change the position or angle of the original on the scanning surface to reduce moiré. However, nowadays most image sensors are equipped with low-pass filters to filter out certain interfering components in the image signal and to block excessive spatial frequencies for the sensor.This low-pass filtering can either be implemented using an optical component in the beam path or can be achieved through electronic signal post-processing.
Another way to reduce moiré is so-called oversampling. The number of pixels is increased compared to the resolution of the output image. This increases the sampling frequency, so to speak, so that there are fewer artifacts and the limit frequency of the sensor is higher than the smallest displayable element.
Related Topics
There are two types of image sensors for industrial cameras on [...]
READ MORE
The Bayer matrix is the spatial arrangement of the red, green [...]
READ MORE
The term megapixel comes from the field of digital photography and [...]
READ MORE